Vitiligo is a chronic skin condition characterized by patches of the skin losing its pigment. The patches of skin affected become white with contrasting margins.
The disease is due to the destruction of melanocytes, the melanin-producing cells in the skin by immune cells.
Vitiligo may be a source of great psychological stress and sometimes stigmatization.
There are several treatment options for vitiligo including sunscreen, makeup, creams and in some cases surgery.
Surgical intervention to treat vitiligo is only recommended when other options have failed and the disease is stable, i.e absence of new lesions and absence of the spread of existing lesions in the past 1 – 2 years.
Indications of Vitiligo Surgery
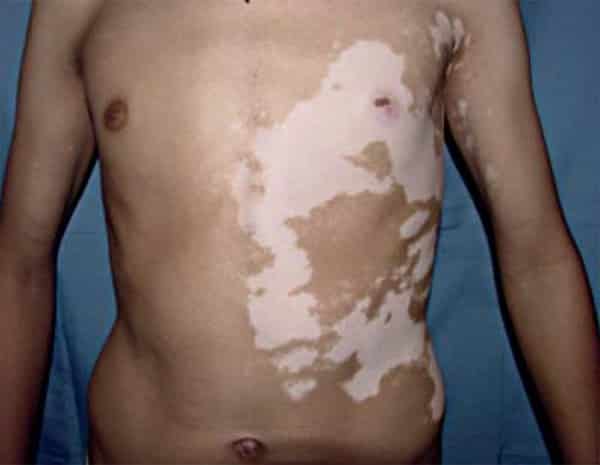
segmental vitiligo
Surgery in vitiligo is indicated in patients with stable or segmental vitiligo not responding to medical treatment or causing severe psychosocial distress. It can also be performed in patients with leukoderma due to burns, piebaldism, inactive discoid lupus erythematosus, and other stable disease states causing permanent depigmentation.
More: Lipoma Removal Surgery
Vitiligo Surgery
The surgical techniques are collectively known as grafting procedures and they have become a popular choice among dermatologists. It involves the transplantation of healthy pigment cells (melanocytes) from another part of the body to the affected areas.
There are several ways to transplant healthy melanocytes in patients with stable vitiligo.
The choice of the grafting procedure to be performed usually depends upon the extent or size of the vitiligo lesion to be treated, the site of the lesion, the age of the patient, his/her expectations and social needs, and lastly the expertise of the operating surgeon. The most common grafting techniques include:
1. Punch grafts (small plugs of skin are transplanted to holes created in the white spots)
Punch grafting is the simplest and the least expensive of all the grafting procedures in vitiligo. The procedure involves the transfer of circular pieces or punches of skin tissue from the donor area into similarly shaped pits that are made on the recipient’s skin.
The size of these punches can range from 1 mm to 2 mm and they are spaced 5-10 mm apart on the recipient’s skin.
2. Split thickness skin grafts (larger pieces of skin are transplanted to white spots where the skin has been removed)
In this technique, thin split-thickness skin grafts are harvested from the pigmented donor area and transplanted at the recipient sites as continuous sheets of tissue grafts.
The advantages of split-thickness skin grafting are that pigmentation can instantly cover larger areas over a short period of time as compared to other techniques. However, prolonged hyperpigmentation is commonly seen, particularly in the exposed areas in dark-skinned patients.
3. Blister grafts (blister roofs from normal skin are transplanted to white spots where other blister roofs were removed)
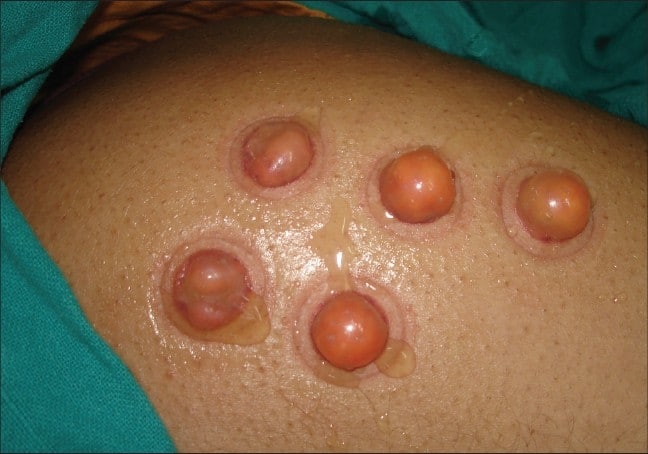
Blister grafting involves the formation of epidermal blisters by application of negative pressure to the normally pigmented skin.
After blister formation, the depigmented epithelium is removed and the roofs of the pigmented donor blisters are transplanted to the affected lesional areas. This type of vitiligo surgery has been shown to have the highest success rates compared to other techniques.
The advantages of this technique include low cost, absence of scarring and the possibility of reusing the donor site. The disadvantages are that it is time-consuming, painful and not suitable for large areas, uneven surfaces and the palm.
4. Cellular grafts (melanocytes and other skin cells from normal skin are transplanted to white spots where the top layer has been removed by dermabrasion or laser treatment).
The techniques include transplantation of autologous cultured melanocytes, cocultured melanocytes and keratinocytes, and non cultured epidermal cells suspension.
Advances in recipient-site preparation and culturing techniques have greatly improved the efficiency of this procedure, achieving good to excellent repigmentation rates for stable vitiligo.
Complications of Vitiligo Surgery
Like every surgical procedure, vitiligo surgery has its own risk of complications. This include
– infection
– bleeding
– hyperpigmentation
– incomplete pigmentation
– perigraft halo
– Cobblestoning
– graft rejection
Recovery
In general, anyone with vitiligo must avoid being in the hot sun. Wearing protective clothing and the use of high-factor sunscreen will be of help.
Avoid getting skin injury as white patches tend to increase in the injured area. Other than these, there are no specific measures to be taken care of post any treatment for vitiligo.
However, regular monitoring of Autoimmune conditions and thyroid function is necessary. Also, care is to be taken in a case of psychological depression.
Vitiligo is not completely curable, and treatments can only minimize the visible white patches and improve skin conditions. Hence, continual monitoring is required, and the treatments are to be repeated according to the advice of a dermatologist.
Vitiligo Surgery Cost
The total cost for vitiligo surgery depends on a lot of factors such as the anesthetic fee, private hospital fee, private operating facility fee and extent of surgery required.
Most often than not, vitiligo surgery cost is considered a cosmetic procedure and as such is not something that is covered by insurance plans.
The total cost of the procedure is around $4000.
More: Hair Transplant Surgery