Breast Augmentation Surgery
Breast Augmentation Surgery or so-called mammoplasty is a type of cosmetic surgery procedure that uses implants (saline, silicone) or fat tissue (breast lipofilling) to change the size and shape of breasts.
Mammoplasty is performed for different types of indications
Dissatisfaction with the size and shape of her breasts often affects a woman’s emotional well-being. The operation will help in cases when you have:
- The small size of the mammary glands;
- Asymmetry of the mammary glands of a congenital or an acquired nature;
- Change in size and shape of the breast in the postpartum period.
- Deformation of the mammary glands after removal of neoplasms, surgical interventions for mastitis.
- Sagging Breasts- Over time, the breast frame, which is called the Cooper System or Cooper’s Ligaments, stretches and becomes thinner since the amount of collagen declines with age, gravity further enhances this effect. This phenomenon significantly affects the breast contour. Breast enhancement can give patients the youthful shapes they desire, however, if the sagging is advanced, separate breast lifting surgery will be required.
Breast Augmentation Surgery – Approaches
The natural shape of the breast is achieved thanks to the different ways of placing the implants. They can be placed both under the breast tissue and under the pectoral muscle.
Implant under the gland/implant under the muscle
Postoperative scars remain for life. For them to be unobtrusive, the doctor chooses the optimal access, taking into account individual characteristics: the condition and shape of the mammary glands, the patient’s constitution.
There are three types of access that are used:
Sub-breast (inframammary) – involves placing a suture in a natural fold under the breast. This is the most common method – the surgeon has full visual control over the operation process, which reduces the risks. An experienced plastic surgeon places a thin, barely visible suture.
Axillary (axillary) – usually used when the implant is inserted under the pectoralis major muscle. In this case, the incision is made in the natural folds of the armpit skin. Such a seal is practically invisible in any position of the body. The method, which has limitations in the choice of implants, is more often used in patients with very small breasts.
Areolar – in this method the tip of the breast is cut open and implants can be placed under the breast muscle or breast tissue, allowing you to make even a fresh scar invisible. The incision for insertion of the implant runs along the lower half of the areola. This method is often used in combination with areola correction.
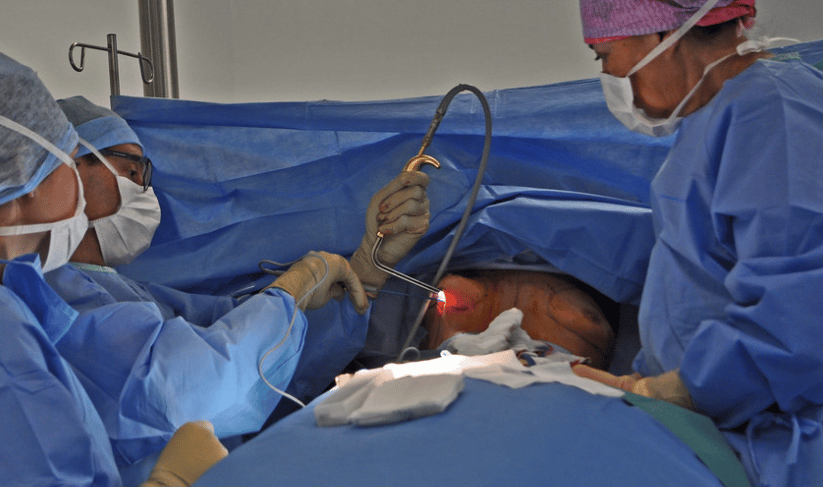
Breast Augmentation Surgery
What are the Types of Breast Implants
Implants can differ according to content, shape, volume and texture.
There are 2 main types of breast implants
Saline-filled implants are silicone shells that are filled with sterile salt water (saline) which has been sterilized. In fact, some of them are filled before the surgery and others are filled during the implant operation.
Two key benefits of saline implants are that it has flexible sizes so you can customize the appearance you want and it has easy leak detection compared to silicone implants. The leak is harmless since it can be absorbed by the body without any concern. Plus saline implants can be used for females of 18 years of age while for silicone implants the minimal age is 22.
Drawbacks – such implants are subject to replacement as they are more likely to lose shape over time.
Silicone-filled implants are pre-filled according to the desired size with silicone gel — a thick, highly cohesive (sticky) fluid that closely mimics the feel of human breast fat. Most women believe that silicone breast implants look and feel more like natural breast tissue.
The greatest benefit of silicone implants is that the gel very closely mimics real breast tissue giving patients a natural look and feel of breasts. While saline implants can become quite firm and feel uncomfortable and look unnatural, especially if used in large volumes.
One notable disadvantage of silicone implants is that, with silicone, the implant doesn’t deflate if a leak occurs. Since it’s harder to detect this complication routine follow-up appointments and imagining tests like mammograms, breast ultrasound and breast MRI are required regularly to monitor these implants to ensure they’re properly functioning. In case the rupture does occur removal of silicone gel is required.
Breast Augmentation Surgery – Implants
Shape
There are 2 main types of implant shapes that patients can choose from. These are
Round – in the form of hemispheres; Anatomical – natural teardrop shape; In fact, it’s the most commonly used implant shape since it’s known to give a more natural look.
The choice of the shape and volume of implants is carried out by the doctor based on measurements and depends on the shape and condition of the patient’s breast, their wishes and aesthetic requirements
Size
The choice of breast implant size depends on several factors like patients existing breast size, personal goals, and surgeon’s recommendations.
The most commonly used size for breast implants is between 350 to 400 cc. Although they can range from 150-800c and even more. Some require different-sized implants to correct existing asymmetry.
Texture
Smooth – rarely used, only for special indications;
Textured – they are used almost always since they have a rough porous surface that adheres to scar tissue that develops after surgery, this reduces the likelihood of capsular contracture and implant displacement.
Fat transfer
The use of autologous fat for breast augmentation is a relatively recent and at the same time effective surgical method. Lately, fat transfer surgeries have become much more popular than they used to be.
Fat transfer essentially transfers fat from other areas of the body using liposuction and injecting it into your breasts. This is an option for females who are looking for a relatively small increase in breast size.
Implant placement
Implants can be placed in 2 places
- Subglandular – Under the breast tissue. Operation and recovery may take less time. Breasts usually hurt less as they heal If a second operation is needed, it will be easier to carry out.
- Submuscular – Under the pectoralis major muscles. Allows to increase the thickness of the tissue above the implant, especially in the upper pole of the breast; this makes the implant less visible and the risk of creasing can be reduced. Also, this approach is associated with a reduced risk of capsular contracture
Which method to choose is decided by the doctor in each case individually.
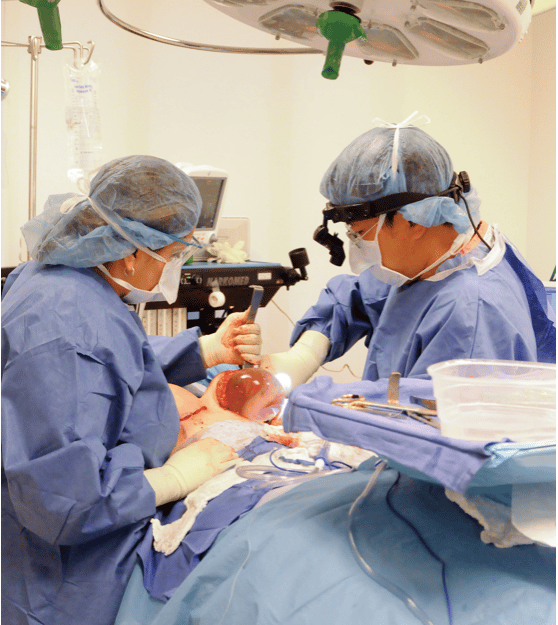
Breast Augmentation Surgery
Before Breast Augmentation Surgery
Before the operation, it is necessary to consult a plastic surgeon. During the appointment, the doctor will exclude the main contraindications to breast implantation, discuss the methods of surgery, select the optimal type, size and shape of the implants.
The patient tells the doctor the exact complaints about their breasts and their expectations from the surgery. Some clinics even suggest making a 3D model of the desired appearance of breasts.
It is important to evaluate complete information about chronic and previous diseases patients suffered from, about all surgeries that you have had in your life before and allergic reactions to choose the medications appropriately.
In addition, a preoperative medical examination will be required. It includes laboratory tests, ultrasound of the mammary glands or mammography, x-rays of the lungs (fluorography) and consultation of doctors – therapist and anesthesiologist.
During Breast Augmentation Surgery
The operation is performed under general anesthesia and usually takes about 1.5–2 hours.
Before starting the operation, the doctor marks the patient in an upright position.
After the introduction into anesthesia, the skin of the mammary glands is disinfected.
Then, an incision is made according to the previously applied markings, surgeon will separate breast tissue from the muscles and connective tissue in that way a cavity is formed to accommodate the implant. Depending on the method, the pocket is located under the mammary gland or the pectoralis major muscle.
Next, the doctor installs an implant. The control of the position of the implants is carried out in the sitting position.
The final stage is the application of cosmetic sutures. If necessary, drainages are installed.
After Breast Augmentation Surgery
Experienced surgeons, modern methods and technological equipment of operating rooms allow performing breast augmentation surgery with minimal risk of complications.
Postoperative period: the first 1-2 weeks require maximum rest, it’s necessary to exclude any type of straining physical activity, especially on the shoulder girdle. During this period, painful sensations are possible to be experienced, aggravated by physical exertion, discomfort – a feeling of heaviness, bursting.
These sensations are associated with an increase in the volume of the mammary gland and they gradually disappear. Postoperative sutures are usually removed on the 8th – 10th day or self-absorbable suture materials are used.
In the postoperative period, any physical activity on the upper shoulder girdle (swimming, tennis, push-ups, etc.), vertical load (running, riding) is strictly prohibited.
The rehabilitation period lasts 1–2 months. At this time, almost constant wearing of compression underwear is required, limiting physical loads. For quick and successful recovery after the intervention, it is important to follow all the doctor’s recommendations. The final results of mammoplasty can be assessed 6–12 months after surgery.
Results of Breast Augmentation Surgery
The result of the operation depends not only on the skill of the plastic surgeon but also on the initial state and structure of the mammary glands: the volume of the subcutaneous fat layer, the presence of breast ptosis (ptosis), scars, asymmetry and general condition.
In some cases, a doctor may recommend a nipple and areola correction or a breast lift in addition to implantation.
However, it is worth remembering that not all deformations can be one hundred percent corrected. Minor asymmetries may persist after surgery, but they will no longer be so noticeable.
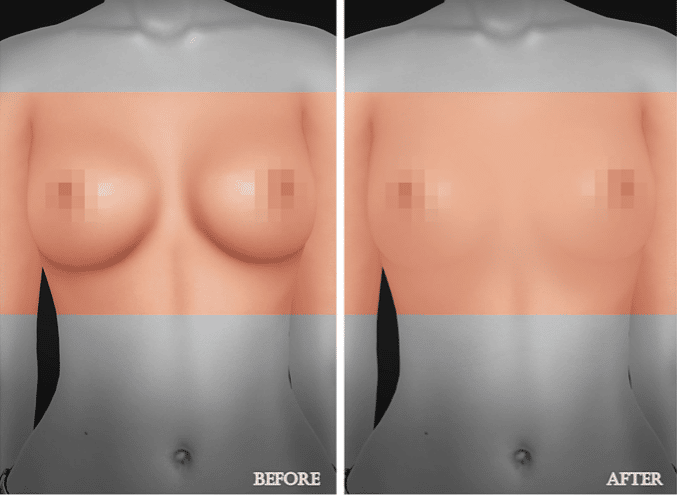
Breast Augmentation Surgery – Before and After
Cost of Breast Augmentation Surgery
The cost for breast augmentation surgery depends on the clinic, the experience of the surgeon and the type of implant that’s used, typically it ranges from 3,300$ to 15,000$.
A consultation fee may or may not be applied towards procedure costs. Since it’s considered to be cosmetic surgery, insurance usually does not cover breast augmentation.
Complications:
- Capsular contracture – scar tissue can form which changes and distorts the shape of the breast implant.
- Changes in nipple and breast sensitivity – the patient may even have breast pain but the good news is this symptom is often temporary
- Silicone Rupture – the risk is higher with saline implants than with silicone gel-filled implants. Patients might require imagining tests like MRI scans or ultrasound to identify the rupture since the physical symptoms are not that significant to detect changes. FDA Recommends routine screening with MRI 5-6 years after placement to screen for silicone breast implant rupture
- Implant position changes
- BIA-ALCL – Breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma – is a rare long-term complication, which is different from the commonly encountered breast cancer, since it comes from scar tissue surrounding the implant. Symptoms can be various, including fatigue, brain fog, muscle or joint pain
Contraindications to Breast Augmentation Surgery
- Age under 18 – Breast augmentation can only be performed if the female has reached puberty since it is at this time that the mammary glands take on their final shape.
- Presence of chronic or acute infectious diseases
- Pathologies affecting blood clotting and coagulation.
- Breast cancer – Women with existing cancer or precancer who have not received adequate treatment.
- Pregnant Females
- Breastfeeding mothers – at least six months should pass after the mother has stopped breastfeeding for surgery to be performed
- Weakened immune system – because of chemotherapy, medications, etc
- Autoimmune diseases
Facts to consider:
- Breast Implants are not permanent – in most cases, no matter the type, implants need to be removed or replaced after some time. The longer patients keep the same implants the higher risk of complications. According to The American Society of Plastic Surgeons “In some cases, the outside shell of the implant breaks down causing silicone to leak and the scar tissue around the implant to harden. It is important to understand for that reason your implants should be removed or exchanged every 10 to 15 years”
- Know your Implants – Make sure to read and understand the labeling of implants which contains information from manufacturers, since they might require special care (e.g rupture screening recommendations for silicone implants)
- Monitoring – it’s the surgeon’s job to warn you about the probable complications and ways to identify them but it’s the patient’s job to be attentive with the symptoms and constantly lookout for problems like infection, pain, swelling, or any change in the shape of appearance. As already mentioned, silicone implants require special attention since their rupture can only be detected using imaging techniques like mammograms, ultrasound and breast MRI, this makes routine screenings necessary.
See Also
References:
https://www.webmd.com/beauty/cosmetic-procedures-breast-augmentation#1
https://www.plasticsurgery.org/cosmetic-procedures/breast-implant-removal
https://aedit.com/procedure/breast-augmentation-augmentation-mammaplasty/cost


