Lumpectomy – Overview
Lumpectomy is the surgical removal of a lump in the breast to treat a malignant tumor or breast cancer.
During the procedure, only the cancerous cells are removed hence it’s more conservative and preferred to more disfiguring option as in mastectomy which involves complete removal of the breast.
A lumpectomy is usually recommended to patients whose cancer has been detected early and who do not have enlarged tumors
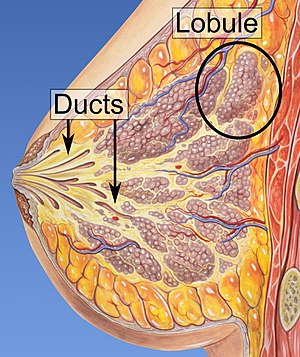
Indications of Lumpectomy
Lumpectomy is used to treat ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), also known as intraductal carcinoma, is a pre-cancerous or non-invasive cancerous lesion of the breast.
DCIS is classified as Stage 0. It rarely produces symptoms or a breast lump one can feel, typically being detected through screening mammography.
After a lumpectomy is performed for DCIS, local radiation therapy is typically performed to help eliminate microscopic-level disease and reduce the possibility of a recurrence.
Lumpectomy Procedure
The surgery takes about 20 -40 minutes and is performed under general anesthesia. The procedure is usually performed with a kind of electric scalpel that uses heat to minimize bleeding (an electrocautery knife).
Most surgeons use curved incisions (like a smile or a frown) that follow the natural curve of your breast and allow for better healing. If the tumor can be seen or felt, the surgeon will remove it along with a rim of healthy tissue around it.
Sometimes, but not always, a rubber tube called a drain will be surgically inserted into the breast area or armpit to collect excess fluid that can accumulate in the space where the tumor was.
The drain is connected to a plastic bulb that creates suction to help remove the fluid. Finally, the surgeon will stitch the incision closed and dress the wound.
Radiation is usually used in conjunction with the lumpectomy to prevent future recurrence. The radiation treatment can last five to seven weeks following the lumpectomy. Although the lumpectomy with radiation helps to decrease the risk of the cancer returning, it is not a cure and cancer may still come back.
MORE: How to Cure Breast Lump without Surgery
Lumpectomy Risks and Complications
Like all surgeries, lumpectomy carries certain risks. Risks associated with all types of surgery include bleeding, infection and hematoma.
The more specific risk with lumpectomy include:
Loss of sensation: There is usually some numbness and loss of sensation in part of the breast after lumpectomy, depending on the size of the lump removed. Some or most of this ability to feel can return.
Breast Asymmetry: This refers to breasts that don’t match exactly. The breasts may not match precisely in size and shape after surgery. This is because removing breast tissue during surgery usually makes the affected breast appear smaller.
Lumpectomy Cost
The total cost for breast lump removal surgery depends on a lot of factors such as the anesthetic fee, private hospital fee, private operating facility fee, size of lump and insurance coverage.
Since each patient’s insurance coverage is different, it’s important to understand your plan to know how much, if any, of the surgery will be covered.
For example, some patients may have high deductibles where insurance will cover only a small portion of the associated costs. On the other hand, some patients may have 80/20 plans where the insurance may cover a significant amount and the patient is only responsible for their copay.
The total cost of the procedure is around $4,341 – $6,590.
MORE: Lipoma Removal Cost